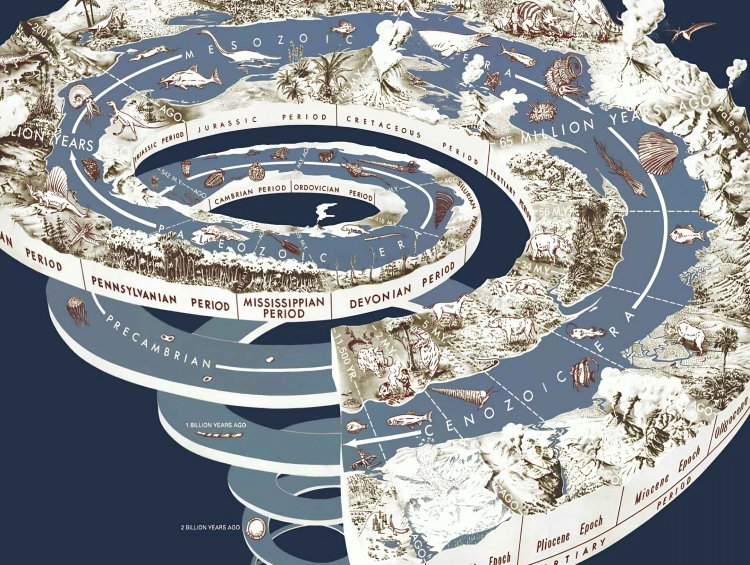
Barite in geochronological dating is a necessary component because it contains trace elements and isotopes that are helpful in establishing age. Barite (BaSO4) is a mineral that often forms in sedimentary environments, hydrothermal veins, or as a precipitate in marine settings. Its purpose is to record the timing of geological events and processes. One important method for dating barite is uranium-lead (U-Pb) dating, which uses the radioactive decay of uranium isotopes to lead isotopes to determine the age of the mineral. This technique is particularly helpful for dating hydrothermal ore deposits and for comprehending the chronology of mineralization events in the history of geology. Depending on the specific geochemical setting, other isotopic systems like sulfur (S), neodymium (Nd), or strontium (Sr) isotopes can also be used to date barite. Geologists require accurate dating of barite samples in order to aid in the reconstruction of tectonic events, geological processes, and the evolution of Earth’s crust over millions to billions of years. Barite is crucial to geochronological dating, which advances our understanding of the dynamics of geological systems and the history of the Earth.
SNDB offers barites which find application in geochronological dating with high quality, competitive prices and hassle free logistics.